In today’s highly regulated pharmaceutical industry, data integrity in pharma has become a critical pillar for ensuring product quality, patient safety, and regulatory compliance. Every decision made during drug development, manufacturing, testing, and distribution is based on data. If that data is incomplete, inaccurate, or unreliable, it can lead to serious consequences such as product recalls, regulatory warning letters, or even risks to patient health.
Regulatory authorities like the US FDA, EMA, MHRA, and WHO emphasize the importance of data integrity in pharma through guidelines, inspections, and enforcement actions. One of the most widely accepted frameworks to maintain data integrity is the ALCOA+ principles, which define the essential characteristics that pharmaceutical data must possess throughout its lifecycle.
This blog provides a detailed explanation of data integrity in pharma, the ALCOA+ principles, regulatory expectations, common challenges, real-world examples, and best practices to achieve sustainable compliance.

What Is Data Integrity in Pharma?
Data integrity in pharma refers to the completeness, consistency, accuracy, and reliability of data throughout its entire lifecycle—from creation and recording to processing, storage, retrieval, and archival.
In simple terms, data integrity ensures that:
Data is trustworthy
Data accurately reflects the actual activity performed
Data has not been altered, deleted, or manipulated improperly
Pharmaceutical data includes:
Laboratory test results
Batch manufacturing records
Equipment logs
Validation and qualification documents
Electronic system data
Audit trails
Quality control and stability data
Maintaining data integrity in pharma is not limited to electronic systems; it equally applies to paper-based records, hybrid systems, and manual entries.
Why Is Data Integrity in Pharma So Important?
The importance of data integrity in pharma cannot be overstated due to the following reasons with GMP guide in pharma.
1. Patient Safety
Medicines are released to the market based on data. Incorrect or falsified data can result in substandard or unsafe products reaching patients.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory agencies expect companies to demonstrate strong controls for data integrity in pharma. Failure can lead to:
FDA Form 483 observations
Warning letters
Import alerts
License suspension
3. Product Quality Assurance
Reliable data ensures consistent manufacturing processes and product quality.
4. Business Continuity
Poor data integrity practices can result in production shutdowns, reputational damage, and financial loss.
Regulatory Expectations for Data Integrity in Pharma
Global regulatory bodies have published specific guidelines emphasizing data integrity in pharma, including:
US FDA – Data Integrity and Compliance With CGMP
MHRA (UK) – GxP Data Integrity Guidance
WHO – Guidance on Good Data and Record Management Practices
EMA – Data Governance and Integrity Expectations
All these guidelines align around one core concept: ALCOA+ principles.
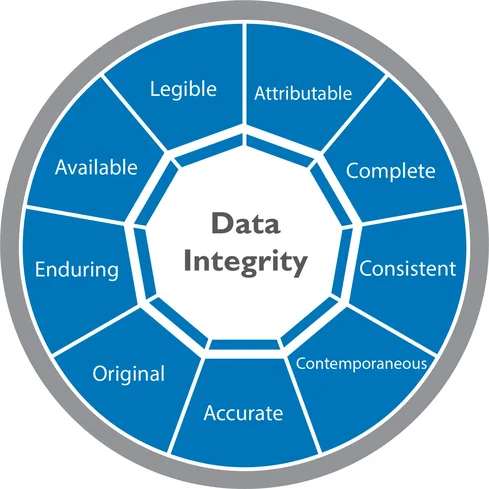
Understanding ALCOA Principles
The foundation of data integrity in pharma is built on the ALCOA principles, originally introduced by the FDA. ALCOA is an acronym representing five key attributes of data.
A – Attributable
Data must clearly indicate who performed the action and when it was performed.
Example:
Signed laboratory notebook entries
Unique user IDs in electronic systems
Poor Practice:
Shared logins
Missing signatures
L – Legible
Data must be readable, permanent, and understandable throughout its retention period.
Example:
Clear handwriting
Proper electronic display
Poor Practice:
Illegible handwriting
Faded ink
Legibility is a critical aspect of data integrity in pharma, especially for long-term record retention.
C – Contemporaneous
Data must be recorded at the time the activity is performed, not later.
Example:
Real-time recording of process parameters
Poor Practice:
Writing data hours or days later
Backdating entries is a major violation of data integrity in pharma.
O – Original
Data should be the first recorded data, or a verified true copy.
Example:
Original chromatograms
Raw instrument data
Poor Practice:
Transcribing results without retaining original data
A – Accurate
Data must be correct, complete, and free from errors.
Example:
Verified calculations
Proper review and approval
Poor Practice:
Unchecked manual calculations
What Is ALCOA+? (Expanded Principles)
To strengthen data integrity in pharma, regulatory authorities expanded ALCOA into ALCOA+, adding four more attributes.
Complete
All data, including repeated tests, failed results, and deviations, must be retained.
Selective reporting is a serious data integrity breach in pharma.
Consistent
Data must follow a chronological order with proper time stamps.
Example:
Sequential batch records
Controlled audit trails
Enduring
Data must be securely stored and preserved throughout its retention period.
Example:
Validated electronic systems
Secure archives
Available
Data must be readily accessible for review, audit, and inspection.
Example:
Easy retrieval during regulatory inspections
Data Integrity in Pharma: Paper-Based vs Electronic Systems
Paper-Based Systems
Challenges:
Illegible handwriting
Backdating
Missing pages
Controls:
Controlled forms
Indelible ink
Line-through corrections
Electronic Systems
Challenges:
Shared passwords
Disabled audit trails
Unvalidated systems
Controls:
Role-based access
Audit trail review
System validation (21 CFR Part 11)
Both systems require equal attention to data integrity in pharma.
Common Data Integrity Issues in Pharma
Some of the most frequently observed data integrity violations include:
Data falsification
Deleting raw data
Repeated testing without justification
Shared user accounts
Backdated entries
Uncontrolled spreadsheets
Addressing these issues is essential to maintain data integrity in pharma.
Role of Audit Trails in Data Integrity
Audit trails are a backbone of data integrity in pharma, especially in electronic systems.
Audit trails must:
Be enabled
Be secure
Capture who, what, when, and why
Be regularly reviewed
Failure to review audit trails is a common FDA observation.
Data Integrity Lifecycle Approach
Data integrity in pharma must be ensured across the entire data lifecycle:
Data generation
Data processing
Data review
Data reporting
Data storage
Data archival
Data retrieval
Each stage must comply with ALCOA+ principles.
Data Governance and Culture
Technology alone cannot ensure data integrity in pharma. A strong quality culture is essential.
Key elements:
Management commitment
Clear SOPs
Employee accountability
Continuous training
Training and Awareness
Regular training programs should cover:
ALCOA+ principles
Good documentation practices
Ethical behavior
Consequences of data manipulation
Training is a preventive measure for protecting data integrity in pharma.
Risk-Based Approach to Data Integrity
Companies should apply ICH Q9 risk management principles to data integrity by:
Identifying critical data
Assessing risks
Implementing controls
Monitoring effectiveness
Best Practices to Maintain Data Integrity in Pharma
Establish strong SOPs
Validate computerized systems
Implement access controls
Review audit trails
Conduct internal audits
Encourage transparent reporting
Maintain backup and disaster recovery
These practices ensure sustainable data integrit
y in pharma compliance.
Regulatory Consequences of Data Integrity Failures
Failure to maintain data integrity in pharma can result in:
Product recalls
Warning letters
Import bans
Loss of market authorization
Criminal liability
Future of Data Integrity in Pharma
With the adoption of:
AI and automation
Digital manufacturing
Cloud-based systems
The scope of data integrity in pharma is expanding, making robust data governance more important than ever.
Conclusion
Data integrity in pharma is not just a regulatory requirement—it is a fundamental responsibility to patients, regulators, and the organization itself. The ALCOA+ principles provide a clear and practical framework to ensure that pharmaceutical data remains reliable, accurate, and trustworthy throughout its lifecycle.
By implementing strong data governance, fostering a culture of integrity, and continuously monitoring compliance, pharmaceutical companies can safeguard product quality, ensure patient safety, and maintain regulatory confidence. In an increasingly digital pharmaceutical landscape, a proactive approach to data integrity in pharma is essential for long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is data integrity in pharma?
Data integrity in pharma ensures data is complete, accurate, reliable, and trustworthy throughout its lifecycle.
2. What are ALCOA+ principles?
ALCOA+ defines attributes that data must meet: Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, Accurate, Complete, Consistent, Enduring, and Available.
3. Is data integrity applicable only to electronic data?
No, data integrity in pharma applies to both paper-based and electronic systems.
4. Why is data integrity critical for FDA compliance?
FDA decisions are based on data. Any compromise can affect patient safety and regulatory approval.
5. How can companies improve data integrity?
Through training, strong SOPs, system validation, audit trail review, and quality culture.